Other Facilities
The Yebes Observatory also has other facilities that are not included in the ICTS catalogue but are essential in its daily operation. Each of them is described below.
1. Microwave and millimetre-wave cryogenic amplifiers lab
The Yebes Observatory laboratories have established themselves as a world benchmark in the accurate measurement of noise from critical elements of receivers used for radio astronomy and space communications
Radio astronomy receivers need extreme sensitivity to being able to detect the weak signals emitted by astronomical sources. This is why it is necessary to have ultra low noise amplifiers of superior characteristics than those commonly used in commercial products. The Yebes Observatory laboratory is fully fitted to carry out the tasks of design, construction and characterization of cryogenic amplifiers that are specially designed to operate at cryogenic temperatures for meeting the strict low noise requirements. It is equipped with closed-cycle cryogenic refrigerators (down to 4K), microwave instrumentation (vector, spectrum and noise analyzers), instruments for characterizing semiconductor devices, assembly equipment (wire bonding and gap machines), welding (binocular and metallographic microscopes), equipment for electrochemical metallization of substrates, etc. Software is also available for both designing microwave circuits and mechanical parts and instrumentation control.
Very low-noise cryogenic amplifiers have been made for numerous frequency bands between 0.1 and 120 GHz, as well as other types of passive microwave components optimized for radiotelescope receivers.
The cryogenic amplifiers laboratory has allowed not only to equip the Yebes Observatory radiotelescopes but also to participate in numerous international projects by making first-rate technical contributions to state-of-the-art instruments (Herschel satellite, ALMA interferometer, IRAM antennas ...). Devices of this type have also been supplied for other related scientific applications, such as ESA deep-space communications, quantum computing, etc. When the application required a significant number of amplifiers or spatial qualification, technological transfers have been made, and advice has been provided to Spanish companies.
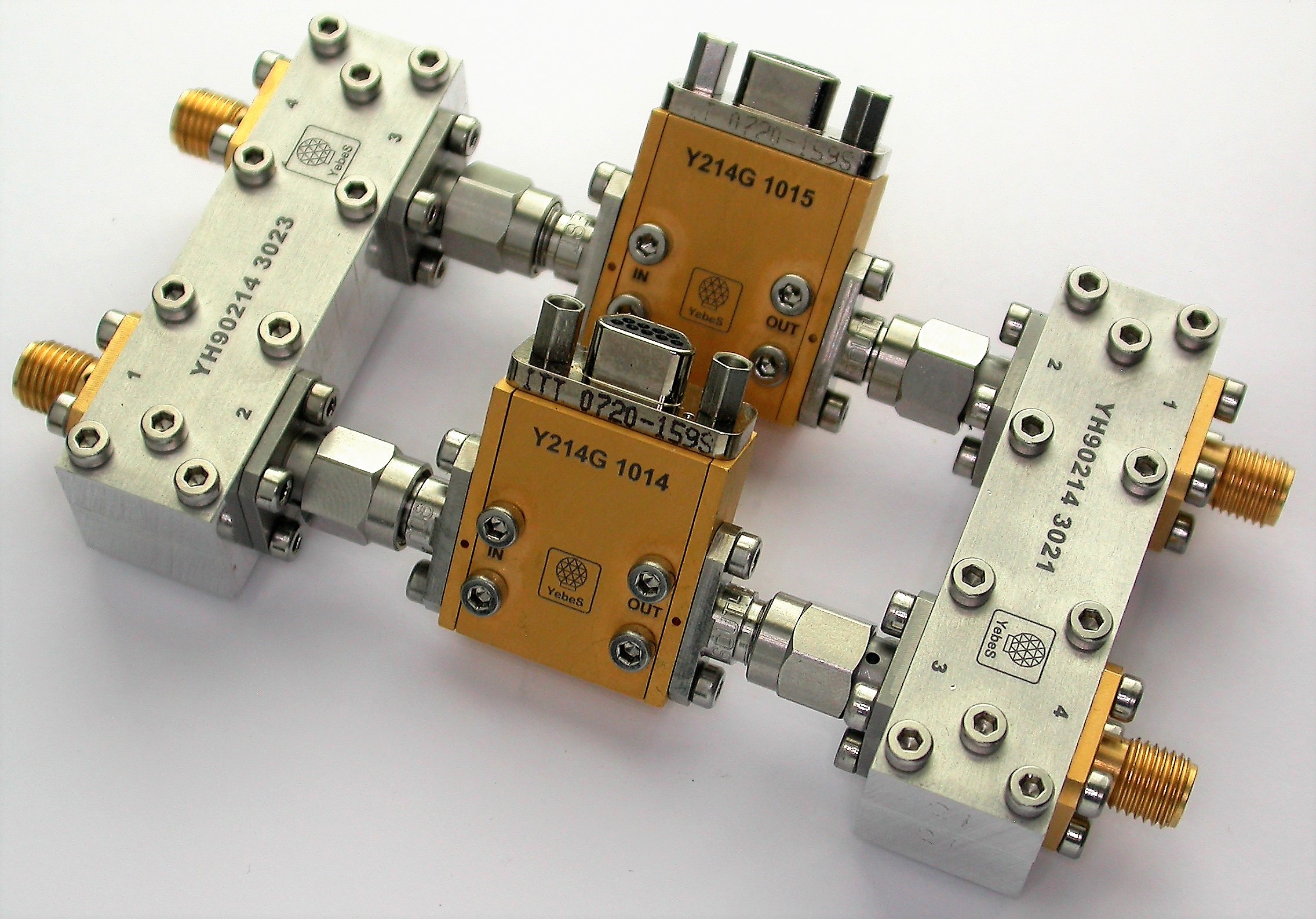
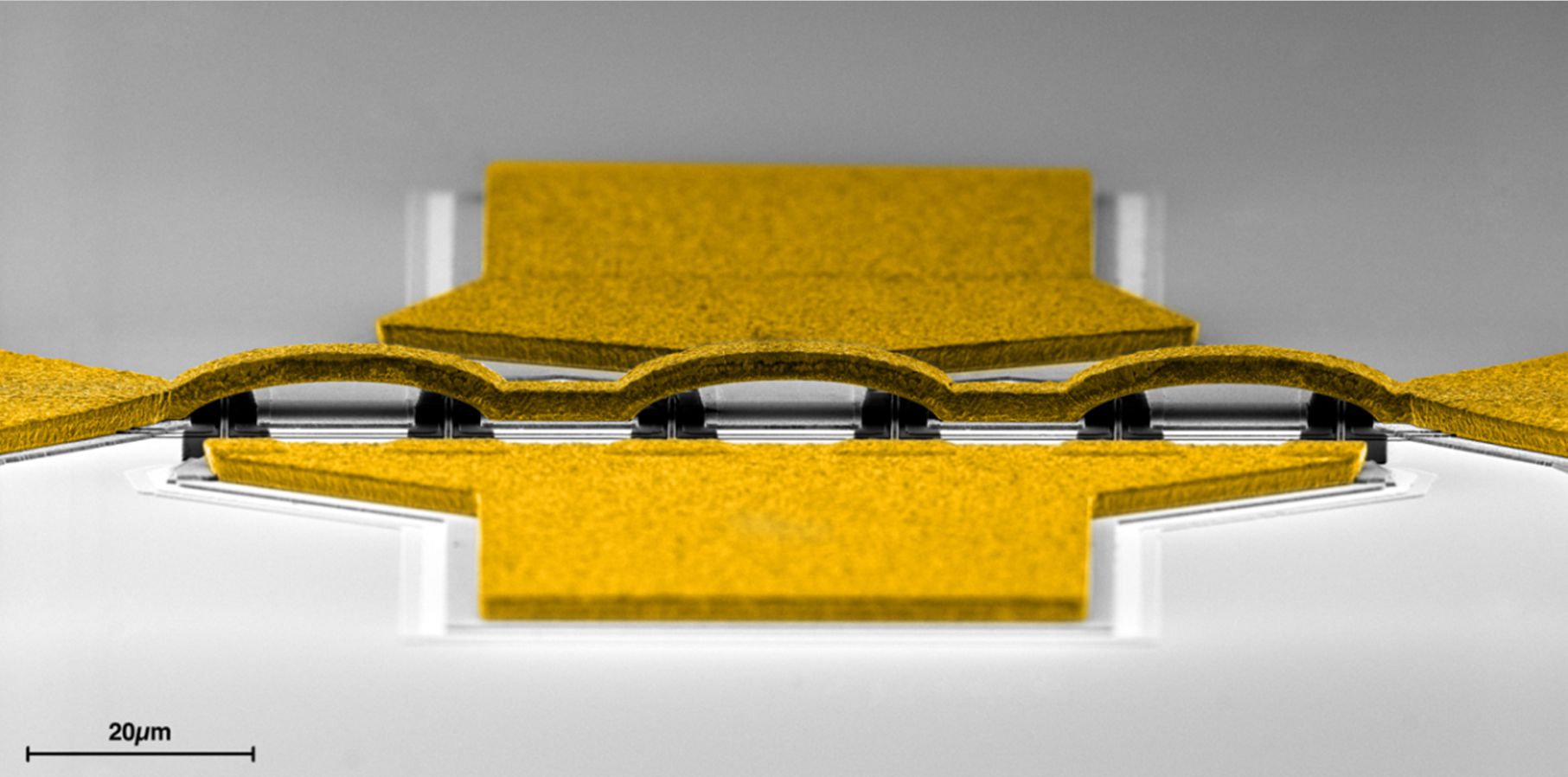
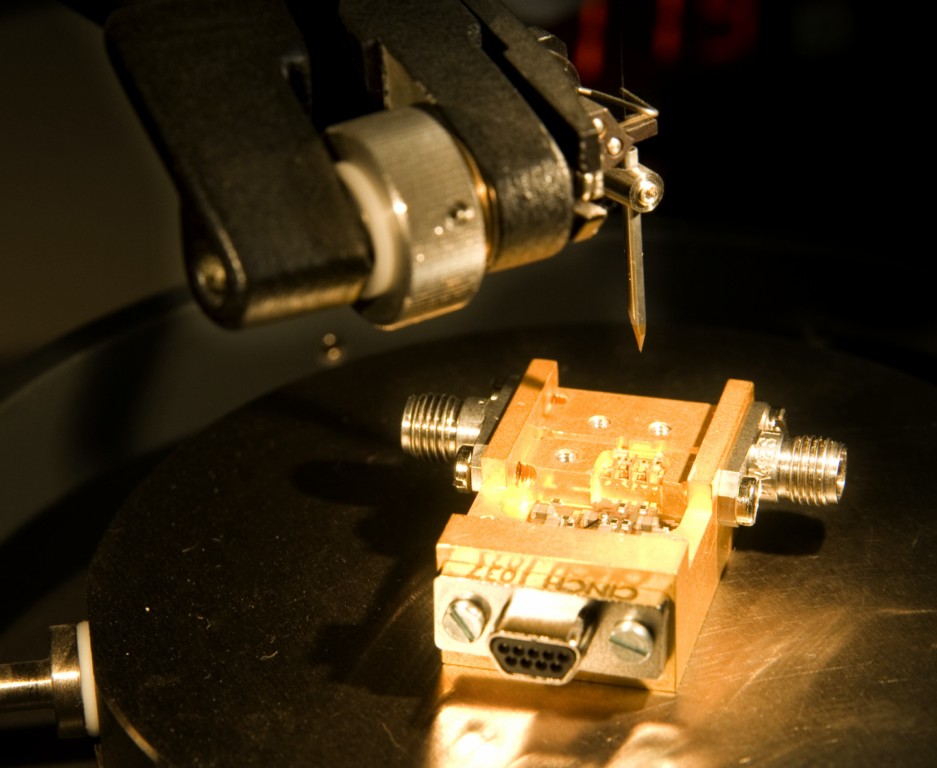
2. Microwave cryogenic receivers laboratory
The Yebes Observatory receiver laboratory has more than 30 years of experience in the design, development, characterization and installation of radio astronomy receivers.
These equipment are highly sensitive radio receivers, necessary to detect the signals emitted by celestial objects. These signals when reaching us, are very weak due to the enormous distances they travel. To achieve high sensitivity, the first stages of the receiver must be cooled down to cryogenic temperatures (approximately -253ºC), so that they add as little noise as possible to the detection of the signal.
This laboratory has developed receivers in the following frequency bands:
-
S band: 2.2 - 2.37 GHz
-
CH band: 3.22 - 3.39 GHz.
-
C band: 4.56 - 6.9 GHz
-
X band: 8.1 - 8.9 GHz
-
K band: 21 - 24 GHz
-
Q band: 31.5 - 50 GHz
-
W band: 72-90.5 GHz y 83-116 GHz..
-
Tri-band: S (2.2-2.7GHz) / X (7.5-9 GHz) / Ka (28-33 GHz) (three simultaneous bands)
-
Wideband (VGOS): 2-14 GHz.
The achieved noise temperatures range from 10 to 40 K, depending on the frequency band.
Furthermore, the laboratory also deals with the development of receiver calibration and control modules and systems for the detection of radio-frequency interference (RFI), as well as the characterization of the surface of large antennas to optimize its parabolic shape and efficiency, using holographic techniques.
It participates in various national and international projects for the development of new types of receivers, such as the Radio net-BRAND project, for the construction of a prototype 1.5 - 15.5 GHz receiver. It also assists several observatories in the development of instrumentation, such as the Norwegian Mapping Authority (NMA), the Finnish Geospatial Research Institute (FGI) or the National Astronomical Research Institute of Thailand (NARIT).
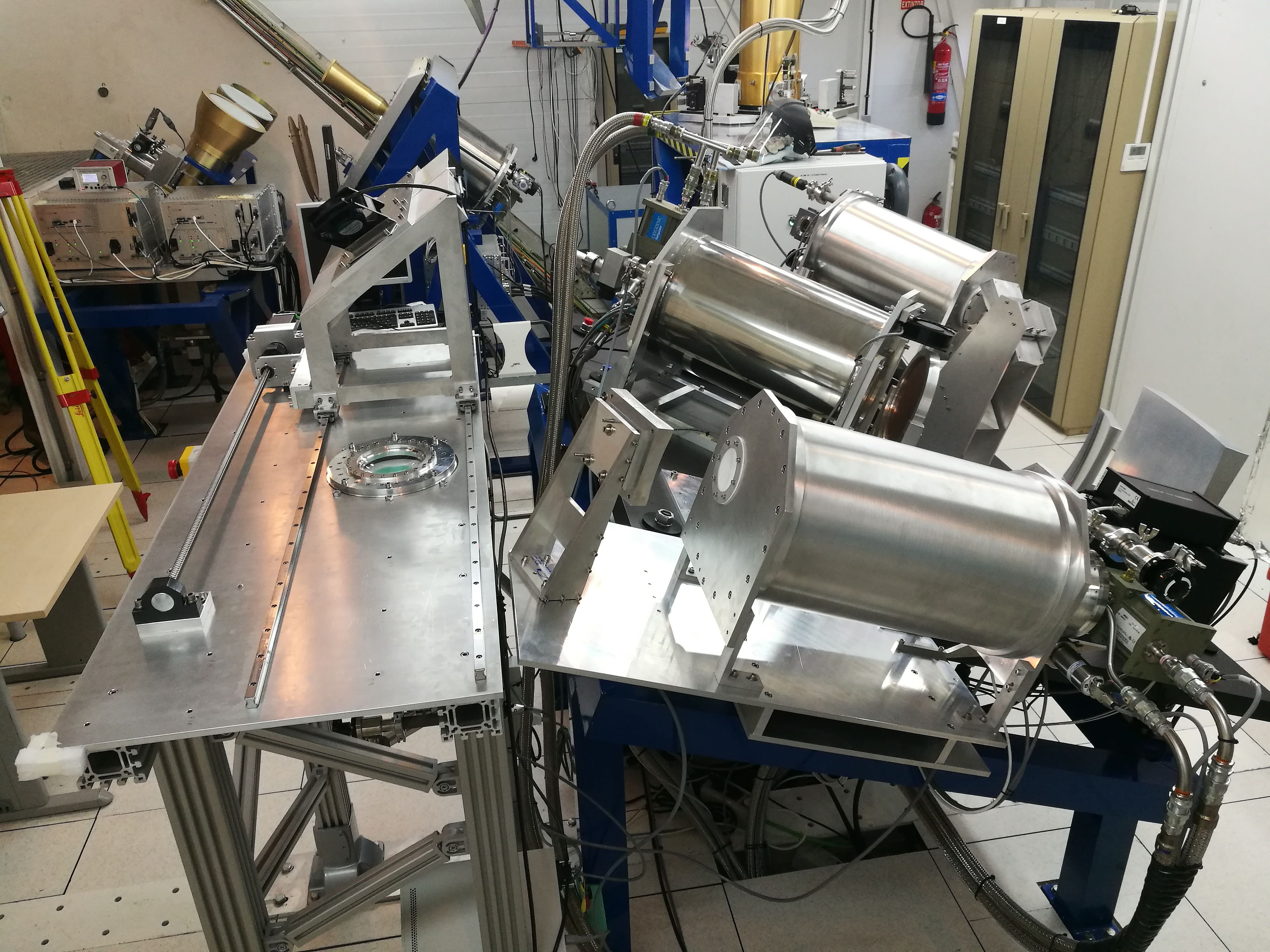


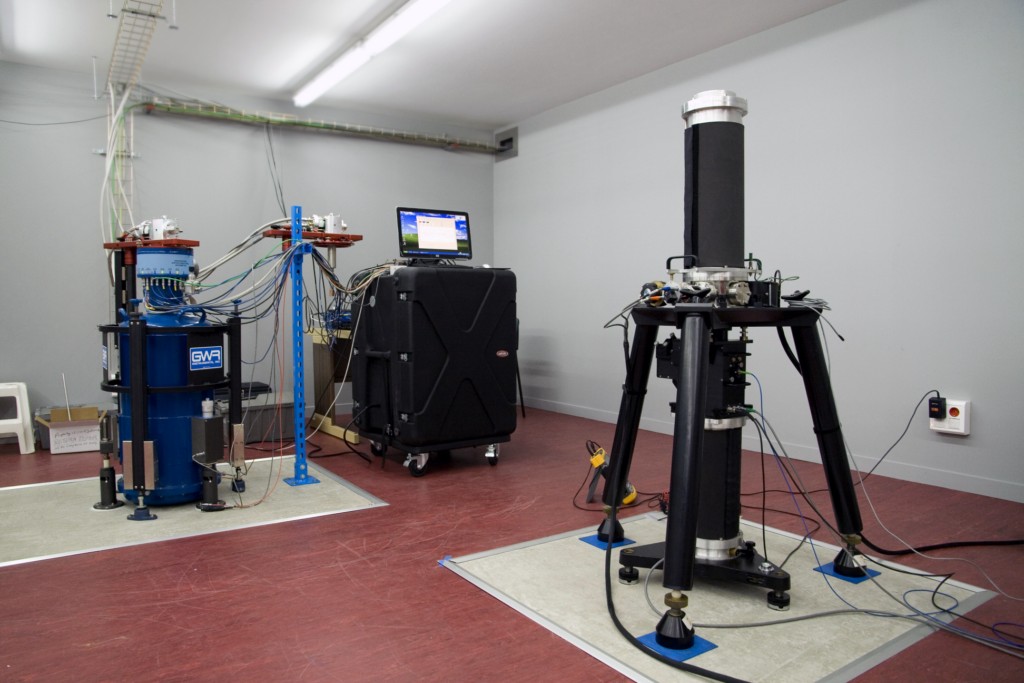
3. Gravimetric pavilion
This building has an interior chamber for the stabilization of its temperature. It contains absolute and relative gravimeters and seismographs that installed on isolated pillars in the internal chamber for the measurement of terrestrial gravity and the detection of earthquakes. It also has a GNSS receiver integrated in an international network, a weather station and an underground water sensor. The data collected by all instruments are sent to servers abroad.
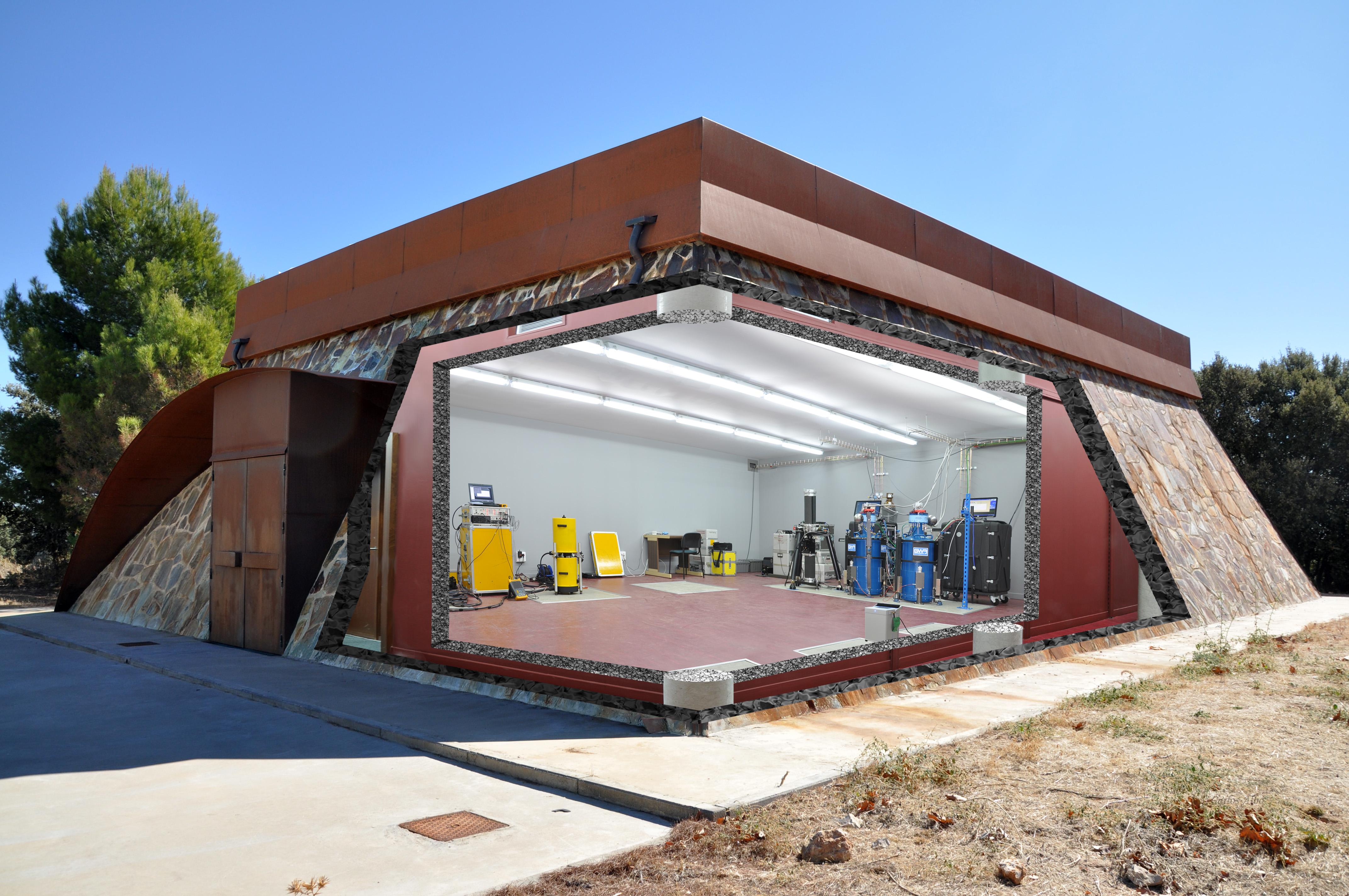


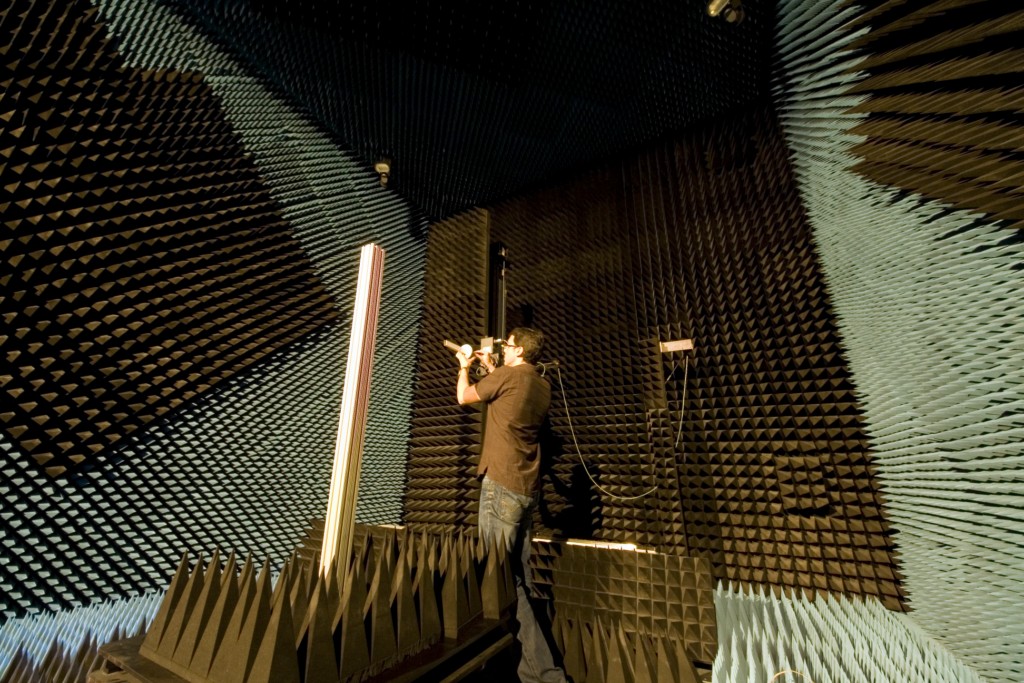
4. Feeds laboratory and anechoic chamber
This building has an anechoic chamber with a frequency operating range from 2 to 140 GHz. Its large dimensions of 11.5x5x5 m allow measurements in both the near and far-field. It uses a 1.83 x 1.823 m size scanner for near-field measurements with a positioning accuracy of 50 um and flatness of 25um. It also has a spherical positioner that allows spherical near field measurements.

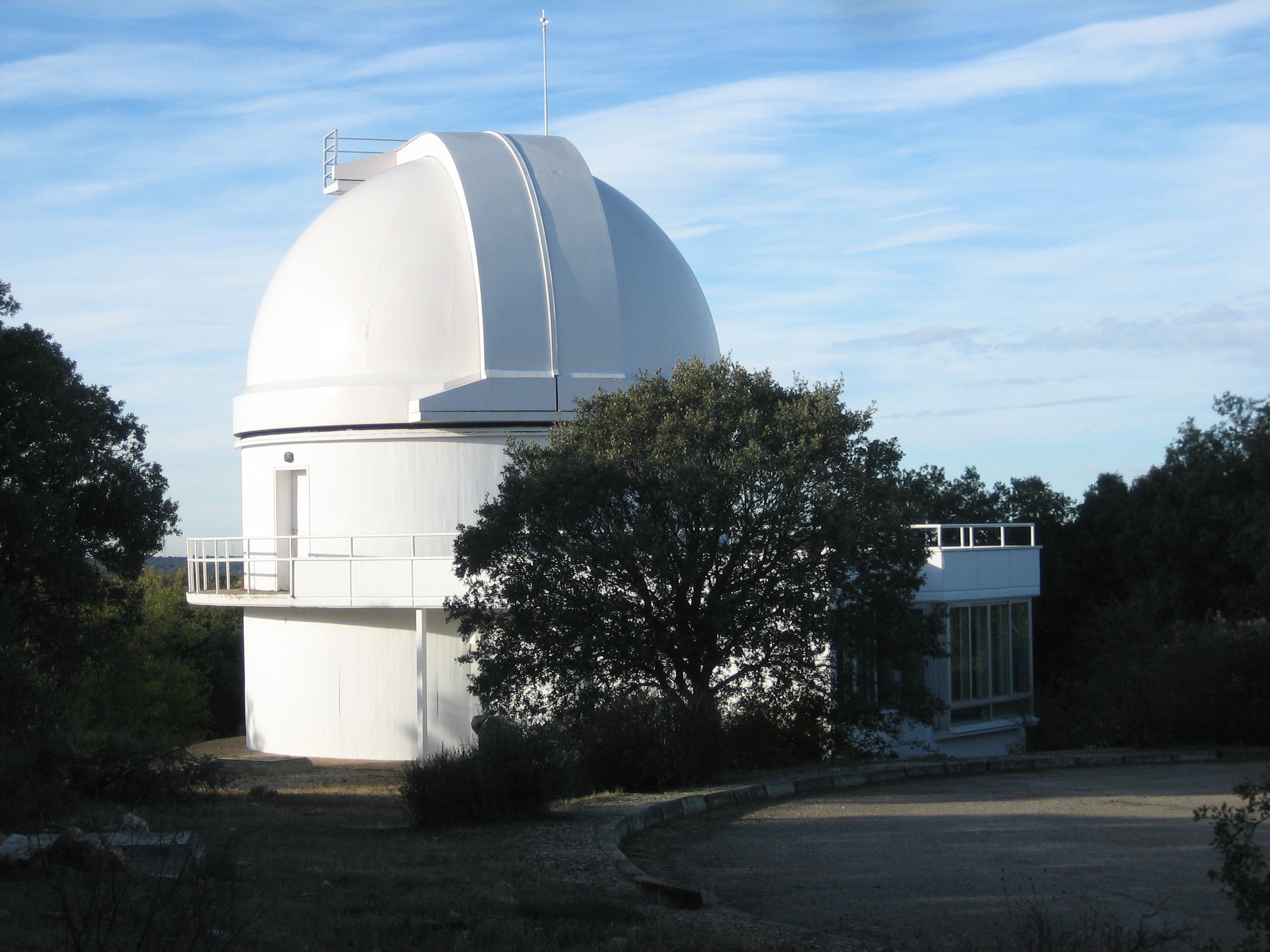
5. Old instruments
The old astronomical observation instruments of the Yebes Observatory date from the 1970s and are a double astrograph with two refractor tubes of 40 cm diameter and a seeker of 20 cm diameter, a solar telescope with a refractor of 20 cm, and a 14 m radio telescope. The group of radio astronomers and engineers at the Observatory started their activities around this last instrument.


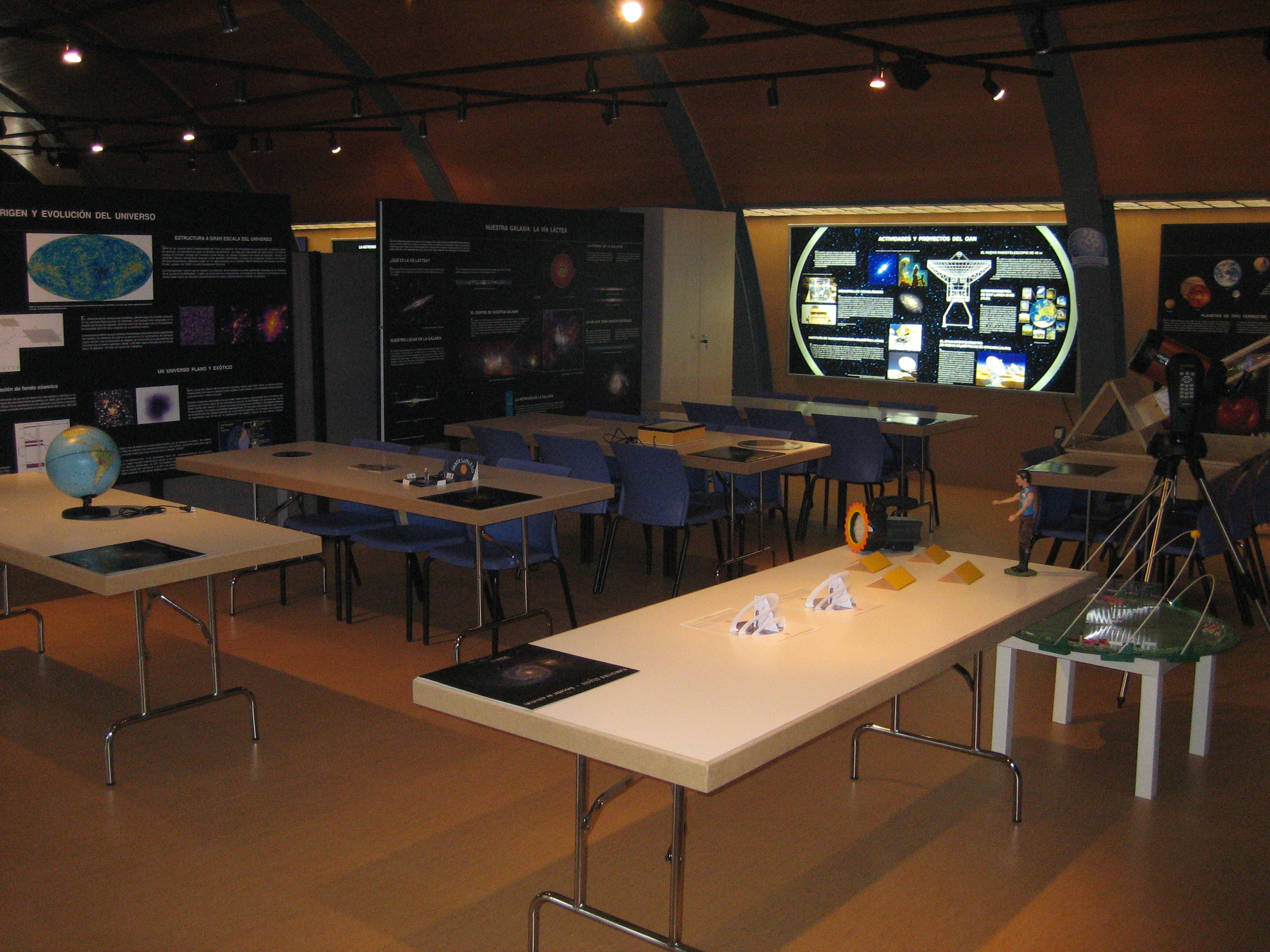
6. Visitors' centre
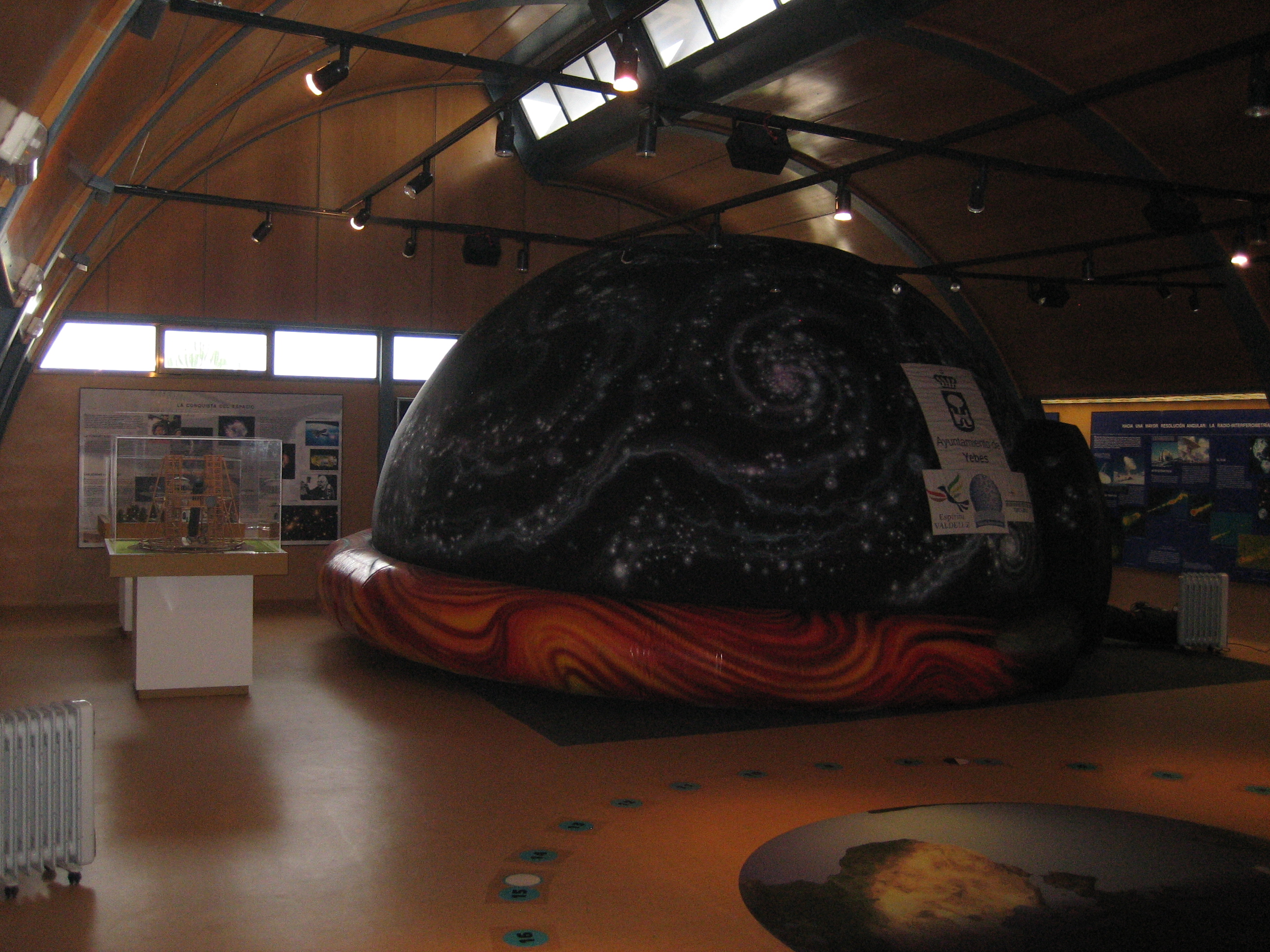
The visitors’ centre houses a permanent exhibition with panels, models, and a small educational radio telescope among other diverse materials from the Astronomy classroom belonging to the Yebes City Council. It also has an inflatable planetarium mainly aimed at schoolchildren and students. The Yebes Observatory maintains an agreement with the Yebes City Council that allows the management of schools and high-schools visits during the week and the general public visits on weekends. More information can be obtained from AstroYebes.




